보스턴 집값 예측하기
이번 내용은 케라스를 이용한 보스턴 집값 예측하기입니다.
데이터셋 가져오기
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from keras.datasets import boston_housing
# 보스톤 집값 데이터 가져오기
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test)= boston_housing.load_data()
데이터를 살펴봅시다.
X_train.shape
(404, 13)
X_test.shape
(102, 13)
훈련데이터는 404개, 테스트데이터는 102개가 있고 모두 13개의 수치 특성이 있습니다.
데이터 정규화
데이터를 정규화하는 이유는 여기서 다루는 데이터가 서로 다른 스케일을 가진 값들이기때문에, 신경망에 주입하게되면 학습을 더 어렵게 만들기 때문입니다. 따라서 특성별로 정규화를 해줍니다.
# 데이터 정규화하기
mean = X_train.mean(axis = 0)
std = X_train.std(axis = 0)
X_train = (X_train - mean)/std
X_test = (X_test - mean)/std
전체 코드
전체코드입니다.
은닉층 유닛에 Re-Lu 활성화 함수를 사용하여 구현했습니다.
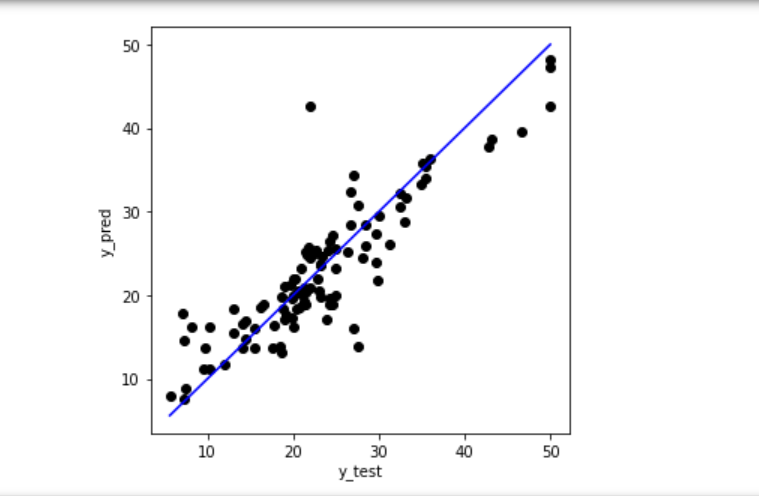
기준선인 직선에 가까울수록 정확한 예측을 한 것으로 볼 수 있습니다.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from keras.datasets import boston_housing
# 보스톤 집값 데이터 가져오기
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test)= boston_housing.load_data()
# 데이터 정규화하기
mean = X_train.mean(axis = 0)
std = X_train.std(axis = 0)
X_train = (X_train - mean)/std
X_test = (X_test - mean)/std
# 순차모델 생성
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
# 레이어 생성
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, input_shape = (13,), activation='relu')) # 입력 + 은닉층
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)) # 출력층
# 컴파일
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='mse', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 모델 학습하기
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=50, batch_size=10)
# 예측
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# 예측 결과 그리기
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.scatter(y_test, y_pred, c = 'black')
plt.plot([min(y_test), max(y_test)], [min(y_test), max(y_test)], c =
'blue')
plt.xlabel('y_test')
plt.ylabel('y_pred')
# 그래프 보이기
plt.show()
댓글남기기